EMEA stands for Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. It’s a geographical designation used by businesses and organizations to refer to this broad region.
What is the Geographical Area of EMEA?
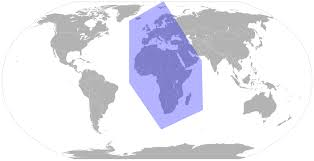
The geographical area of EMEA (Europe, the Middle East, and Africa) encompasses a vast and diverse region:
Europe
- Western Europe: Countries like the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Spain, and Italy.
- Eastern Europe: Includes Russia, Poland, Hungary, and the Czech Republic.
- Northern Europe: Countries such as Sweden, Norway, Denmark, and Finland.
- Southern Europe: Includes Greece, Portugal, and the Balkans.
Middle East
- Gulf States: Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, and Oman.
- Levant: Countries like Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, and Syria.
- Other Middle Eastern Countries: Includes Turkey, Iran, and Iraq.
Africa
- North Africa: Countries such as Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, and Morocco.
- Sub-Saharan Africa: Includes Nigeria, South Africa, Kenya, Ghana, and Ethiopia.
- East Africa: Countries like Tanzania, Uganda, and Rwanda.
- West Africa: Includes Senegal, Ivory Coast, and Mali.
- Central Africa: Countries such as the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Cameroon.
- Southern Africa: Includes Botswana, Namibia, and Zimbabwe.
This region spans four continents: Europe, Africa, Asia, and, due to Greenland, North America. The EMEA region is known for its cultural, economic, and political diversity, making it a significant area for global business and trade.
What is the Geospan of EMEA?
The term EMEA stands for Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. It’s a geographical designation used by businesses and organizations to refer to this broad region. Here are some key points about EMEA:
- Geographical Scope: EMEA includes all European nations, all African nations, and the countries that make up the Middle East. This region spans four continents: Europe, Africa, Asia, and, due to Greenland, North America.
- Business Use: The term is commonly used for sales, marketing, production, and logistics purposes. It helps companies simplify the vast differences in this region and apply similar strategies and budgets.
- Time Zones: Most of the EMEA region falls within four time zones, which facilitates communication and travel for businesses.
- Diversity: EMEA covers a diverse range of cultures, languages, and economic landscapes, making it one of the most ethnically diverse regions.
What Are the Economic Influences of EMEA?
The EMEA region (Europe, the Middle East, and Africa) is a diverse and economically significant area with several key takeaways:
Diverse Economies: EMEA encompasses a wide range of economies, from highly developed nations in Europe to emerging markets in Africa and the Middle East. This diversity offers a variety of investment opportunities and economic dynamics.
- Developed Markets: Countries in Western Europe, such as Germany, France, and the United Kingdom, have well-established economies with robust infrastructure, advanced technology, and stable political environments. These markets offer opportunities in sectors like finance, technology, healthcare, and manufacturing.
- Emerging Markets: Nations in Africa and the Middle East, such as Nigeria, Kenya, and the United Arab Emirates, are experiencing rapid economic growth and development. These markets present opportunities in sectors like telecommunications, renewable energy, agriculture, and real estate.
- Natural Resources: The Middle East is rich in oil and gas reserves, while Africa has abundant mineral resources, including gold, diamonds, and rare earth elements. Investing in these sectors can be highly lucrative, though it often comes with higher risks.
- Innovation Hubs: Cities like Berlin, London, and Tel Aviv are known for their vibrant startup ecosystems and innovation in technology and fintech. These hubs attract significant venture capital and offer opportunities for investment in cutting-edge technologies.
- Consumer Markets: With a growing middle class and increasing urbanization, countries in Africa and the Middle East are seeing rising demand for consumer goods and services. This creates opportunities in retail, e-commerce, and consumer finance.
- Infrastructure Development: Many emerging markets in the EMEA region are investing heavily in infrastructure projects, including transportation, energy, and telecommunications. These projects offer opportunities for investment in construction, engineering, and related industries.
- Tourism and Hospitality: Europe remains a top tourist destination, while countries in the Middle East and Africa are increasingly attracting tourists with their unique cultural and natural attractions. Investing in the tourism and hospitality sector can yield significant returns.
These diverse economic dynamics make the EMEA region a compelling area for investors seeking a range of opportunities across different sectors and markets.
Strategic Location: The region’s strategic geographical location makes it a crucial hub for global trade and commerce. Europe serves as a gateway to both the East and West, while the Middle East connects Asia, Africa, and Europe.
The strategic geographical location of the EMEA region offers several advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
- Trade Hub: EMEA’s location makes it a central hub for global trade, facilitating the movement of goods between Asia, Europe, and Africa. This boosts economic activity and trade opportunities.
- Market Access: Businesses in EMEA have access to diverse markets, allowing them to tap into a wide range of consumer bases and economic environments.
- Cultural Exchange: The region’s position fosters cultural exchange and collaboration, enhancing innovation and creativity.
- Logistics and Transportation: EMEA’s strategic location supports efficient logistics and transportation networks, reducing shipping times and costs.
- Investment Opportunities: The diverse economies within EMEA offer various investment opportunities across different sectors, from technology and finance to natural resources and consumer goods.
Disadvantages
- Political Instability: Some parts of the EMEA region, particularly in the Middle East and Africa, experience political instability and conflict, which can disrupt trade and investment.
- Economic Disparities: The region encompasses both highly developed and emerging markets, leading to significant economic disparities that can affect business operations and investment decisions.
- Regulatory Challenges: Different countries within EMEA have varying regulatory environments, which can complicate compliance and increase operational costs for businesses.
- Infrastructure Gaps: While some areas have advanced infrastructure, others may lack the necessary facilities and services, posing challenges for logistics and business operations.
- Cultural Differences: Navigating the diverse cultural landscapes within EMEA can be challenging for businesses, requiring careful consideration of local customs and practices.
These advantages and disadvantages highlight the complexities and opportunities of operating within the EMEA region.
Resource Richness: The Middle East is known for its substantial oil reserves, which play a significant role in the global energy market. Africa, on the other hand, is rich in natural resources such as minerals and agricultural products.
The resource richness of the Middle East and Africa is indeed remarkable and plays a crucial role in their economies and the global market:
Middle East
- Oil and Gas: The Middle East is home to some of the world’s largest oil and gas reserves. Countries like Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Iran, and the United Arab Emirates are major producers and exporters of petroleum and natural gas.
- Petrochemicals: The region also has a significant petrochemical industry, producing a wide range of chemicals derived from oil and gas.
- Minerals: While oil and gas dominate, the Middle East also has deposits of minerals such as phosphates, used in fertilizers, and various metals.
Africa
- Minerals: Africa is rich in minerals, including gold, diamonds, platinum, and cobalt. Countries like South Africa, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Botswana are major producers of these valuable resources.
- Agricultural Products: The continent produces a variety of agricultural products, including cocoa, coffee, tea, and cotton. Countries like Ivory Coast and Ghana are leading cocoa producers.
- Oil and Gas: Several African countries, such as Nigeria, Angola, and Algeria, have significant oil and gas reserves, contributing to their economies.
- Forestry: Africa’s vast forests provide timber and other forest products, supporting both local economies and export markets.
These resources are vital for the economic development of the Middle East and Africa, providing employment, revenue, and opportunities for growth.
Innovation and Technology: Europe is a leader in advanced industries like manufacturing, technology, and automotive. The region’s focus on innovation drives economic growth and competitiveness.
Here are some key aspects:
- Research and Development (R&D): Europe invests heavily in R&D, fostering a culture of innovation. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK are leaders in scientific research and technological advancements.
- Advanced Manufacturing: Europe is home to advanced manufacturing industries, including automotive, aerospace, and machinery. Innovations in these sectors enhance productivity and global competitiveness.
- Technology Hubs: Cities like Berlin, London, and Stockholm are renowned for their vibrant tech ecosystems. These hubs attract startups, venture capital, and talent, driving technological innovation and economic growth.
- Sustainable Technologies: Europe is at the forefront of developing sustainable technologies, such as renewable energy, electric vehicles, and green manufacturing processes. These innovations contribute to economic growth while addressing environmental challenges.
- Education and Skills: European countries prioritize education and skills development, ensuring a highly skilled workforce. This focus on education supports innovation and the adoption of new technologies.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between governments, academia, and the private sector fosters innovation. Initiatives like Horizon Europe provide funding and support for research and innovation projects.
- Digital Transformation: Europe is embracing digital transformation across various industries, enhancing efficiency and creating new business opportunities. This includes advancements in AI, IoT, and cybersecurity.
These factors collectively drive Europe’s economic growth and competitiveness, positioning the region as a global leader in innovation and technology.
Emerging Markets: Africa presents a burgeoning consumer market with vast potential for growth. The region’s young population and increasing urbanization are driving demand for goods and services.
Africa’s burgeoning consumer market is indeed driving significant demand for various goods and services. Here are some key areas where demand is particularly strong:
- Consumer Goods: With a growing middle class, there is increasing demand for consumer goods such as electronics, clothing, and household items. Brands that cater to the preferences and needs of African consumers are seeing substantial growth.
- Food and Beverages: Urbanization and changing lifestyles are driving demand for processed and packaged foods, as well as beverages. There is also a growing market for healthier and organic food options.
- Telecommunications: The demand for mobile phones, internet services, and related technologies is skyrocketing. As more people gain access to mobile devices and the internet, the telecommunications sector is experiencing rapid growth.
- Financial Services: There is a rising need for banking, insurance, and other financial services. Fintech solutions, including mobile banking and digital payment platforms, are particularly popular as they provide convenient and accessible financial services.
- Healthcare: The demand for healthcare services and products is increasing, driven by population growth and a greater focus on health and wellness. This includes pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and healthcare facilities.
- Education: With a young population eager for education and skills development, there is a growing demand for educational services, including schools, universities, and vocational training centers.
- Real Estate and Infrastructure: Urbanization is fueling demand for housing, commercial properties, and infrastructure development. This includes residential buildings, office spaces, and transportation networks.
- Renewable Energy: There is a growing interest in renewable energy solutions, such as solar and wind power, to address energy needs and promote sustainability.
These demands reflect the dynamic and evolving consumer market in Africa, offering numerous opportunities for businesses and investors.
Trade Relationships: EMEA’s economic growth is bolstered by robust trade relationships within the region and with other global markets. The European Union (EU) serves as a prominent trading bloc, facilitating seamless trade among its member states.
The European Union (EU) is indeed one of the most prominent trading blocs in the EMEA region. Here are some key points about the EU and other notable trading blocs:
European Union (EU)
- Members: The EU consists of 27 member countries, including Germany, France, Italy, Spain, and the Netherlands.
- Single Market: The EU operates a single market, allowing for the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people among member states.
- Customs Union: The EU has a customs union, meaning member states apply a common external tariff on imports from non-EU countries.
- Trade Agreements: The EU has numerous trade agreements with countries and regions around the world, enhancing its global trade relationships.
Other Prominent Trading Blocs in EMEA
- European Free Trade Association (EFTA): Includes Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland. EFTA promotes free trade and economic integration among its members and with the EU.
- Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC): Comprises Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. The GCC focuses on economic and political cooperation among its member states.
- African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA): Aims to create a single continental market for goods and services, promoting intra-African trade and economic integration.
These trading blocs play a crucial role in facilitating trade, economic growth, and cooperation within the EMEA region and beyond.
What is a TRADING Bloc?
A trading bloc is a group of countries that have joined together to promote trade among themselves by reducing or eliminating trade barriers such as tariffs, import quotas, and other restrictions. The main goals of a trading bloc are to increase economic cooperation, enhance trade efficiency, and boost economic growth among member countries. Here are some key features of trading blocs:
- Free Trade Area: Member countries agree to eliminate tariffs and other trade barriers on goods and services traded among themselves. An example is the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).
- Customs Union: In addition to eliminating internal trade barriers, member countries adopt a common external tariff on imports from non-member countries. The European Union (EU) is an example of a customs union.
- Common Market: This goes beyond a customs union by allowing the free movement of goods, services, capital, and labor among member countries. The EU also functions as a common market.
- Economic Union: Member countries integrate their economies further by harmonizing economic policies, such as monetary and fiscal policies. The EU is moving towards an economic union with the adoption of the euro by some member states.
Trading blocs aim to create larger, more efficient markets, increase competition, and foster economic integration among member countries.
These economic takeaways highlight the importance of the EMEA region in the global economic landscape.

